Water: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→Editor) |
(→Editor) |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
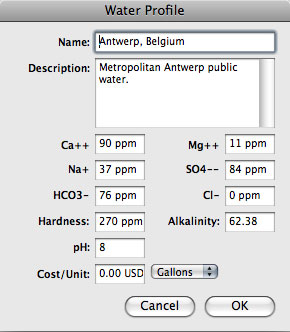
;Hardness | ;Hardness | ||
:Water 'hardness' (including both Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions) is reported as ppm w/v (or mg/L) of CaCO3. Water hardness usually measures the total concentration of Ca and Mg, the two most prevalent divalent metal ions, although in some geographical locations iron, aluminium, and manganese may also be present at elevated levels | :Water 'hardness' (including both Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions) is reported as ppm w/v (or mg/L) of CaCO3. Water hardness usually measures the total concentration of Ca and Mg, the two most prevalent divalent metal ions, although in some geographical locations iron, aluminium, and manganese may also be present at elevated levels. | ||
;Alkalinity | ;Alkalinity | ||
Revision as of 19:46, 26 January 2007
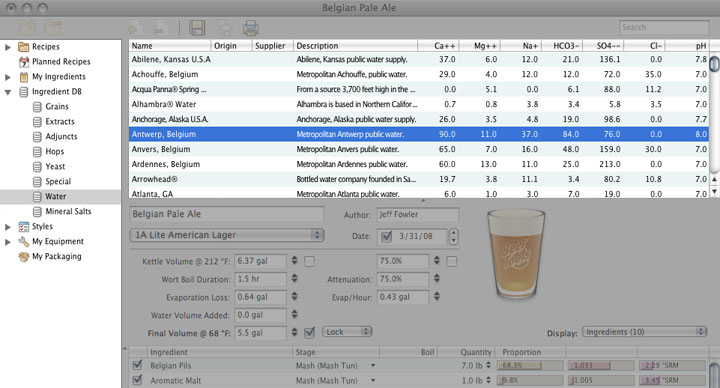
One of the four ingredients of beer. The only requirement for water used in brewing is that it be drinkable. Chemically speaking, brewing water should be non-alkaline and of a certain hardness, prerequisites easily attained with the proper treatment.
Browser
Editor
The various fields in the water editor are used for the following purposes:
|