Vessel: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Vessels are brewing vessels such as | Vessels are brewing vessels such as a kettle, [[mash tun]], and cooler. | ||
==Editor== | ==Editor== | ||
[[Image:vessel.jpg]] | |||
{| | |||
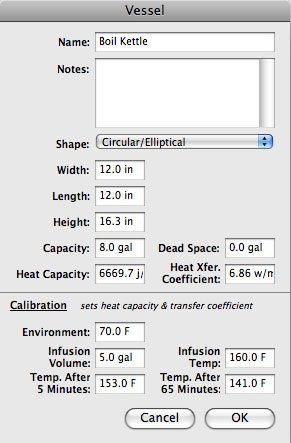
|valign="top"|The various fields in the "Vessel" editor are used for the following purposes: | |||
;Name | |||
:Name of the vessel | |||
;Notes | |||
:useful to mention anything special about this vessel. | |||
;Width | |||
:Add content here | |||
;Length | |||
:Add content here | |||
;Height | |||
:Add content here | |||
;Capacity | |||
:Add content here | |||
;Dead Space | |||
:This is the volume that cannot be drained from the vessel. While in the vessel, the deadspace volume is used in the calculations - including thickness. | |||
;Heat Capacity | |||
:Add content here | |||
;Heat Transfer Coefficient | |||
:Add content here | |||
;Environment | |||
:Add content here | |||
;Infusion Vol | |||
:Add content here | |||
;Temp. After 5 Minutes | |||
:Add content here | |||
;Temp. After 5 Minutes | |||
:Add content here | |||
|valign="top"|[[Image:vessel.jpg|right]] | |||
|} | |||
==Calibration== | ==Calibration== | ||
Latest revision as of 15:38, 31 March 2008
Vessels are brewing vessels such as a kettle, mash tun, and cooler.
Editor
The various fields in the "Vessel" editor are used for the following purposes:
|
Calibration
Here are the basic steps:
- Heat a specific volume of water (measure accurately) in a separate vessel to a temperature in the range normally used for mashing (140-160F or 60-70C)
- Pour the water into the vessel to be tested.
- Check the temperature after 5 minutes in the test vessel.
- Check again after 65 minutes. This measurement determines the vessels heat loss.
Use volumes and temperatures closest to those that you use in your mashing process to achieve more accurate simulation. Enter the measurements in the vessel editor window and the vessel heat capacity will be calculated and inserted for you.